Seiko – Timeless business venture of Kintaro Hattori
The leading Japanese firm Seiko is best to recognize for its optical products, electronic devices, and especially the variety of watches. In fact, the watches/clocks of Seiko had been used as official timekeepers in many intercontinental level sports events including Olympic. As well, the Grand Seiko watch is one of the most loved brands among watch lovers. This watch is considered a tough competitor of swiss watches, those rule the market over the decade. All the credit goes to Kintaro Hattori, a founder, and a top Japanese businessman who set up Seiko as a small shop with a vision to launch a Japanese watch in the market. However, the firm becomes a holding company since 2001.
About the company
It is a famous Japanese firm that had been started as a watch and jewelry shop. Now, the firm also worked as electronics products manufacture that produces electronics devices, optical products, semiconductors, etc. However, Seiko’s main and long-time business is watching and clocks manufacturing and selling. The actual manufacturing of Seiko watches started in 1892. Before that, in 1881, the founder Hattori established a shop to sell watches and jewelry which later on converted into a company. As a matter of fact, the name of company Seiko is a Japanese word meaning success. As per the name, the soon firm achieved success and became one of the leading brands in the market.
The backstory of foundation
A 13 years old Hattori saw a clock shop during his traineeship. That time, he got to know that the clock shop offers income in two ways. One way to get money by selling and the other way is to repair the watches.
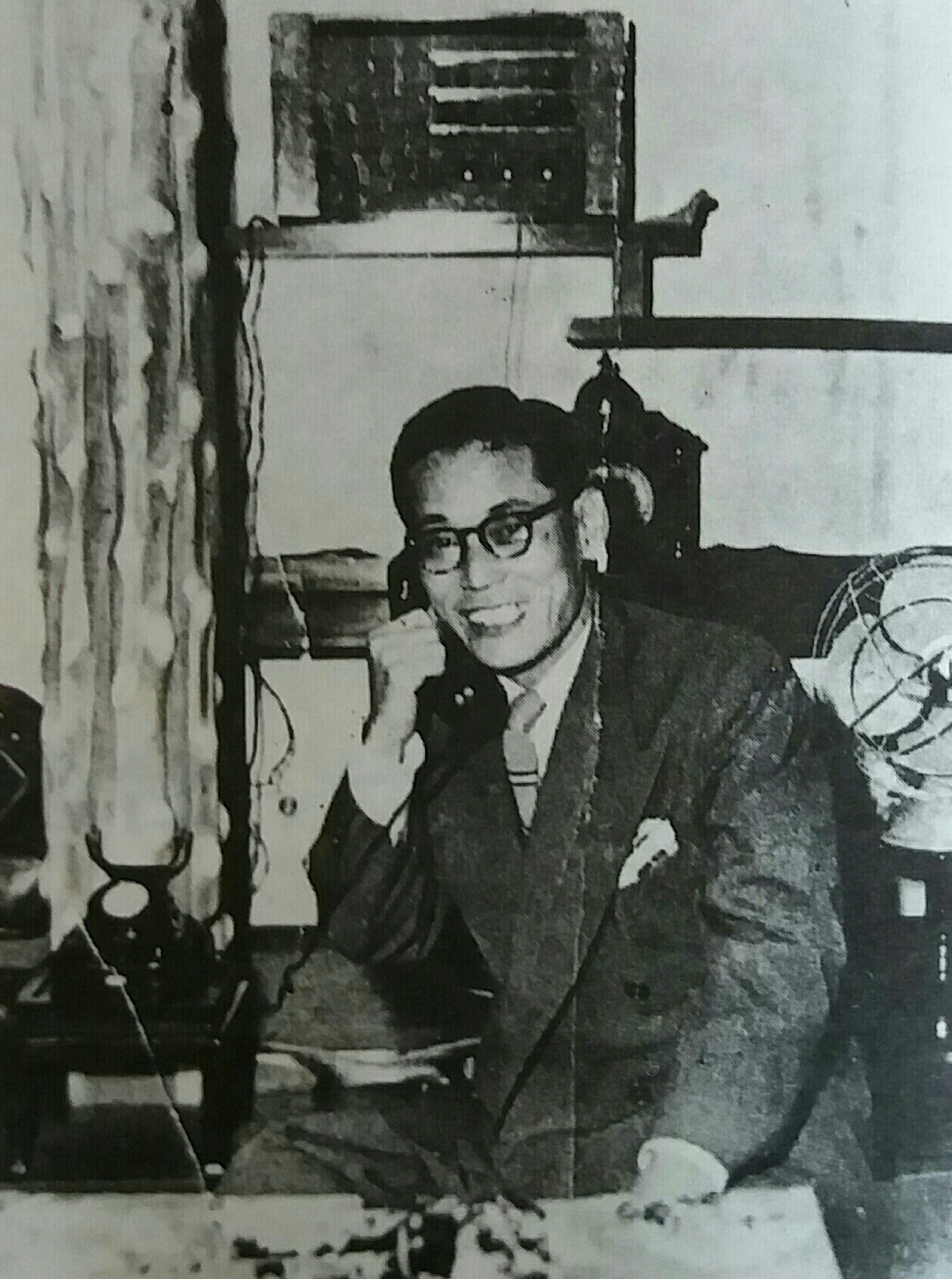
About founder- Kintaro Hattori
In 1881, at the time when Kintaro Hattori was 21 years old, he set up clocks repairing and selling shop in Tokyo. After a few years, he explores the business and established a factory named Seikosha. Sooner or later it is renamed as Seiko.
He was born in Kyobashi, Tokyo in 1860. During his teenage, he started working at sundries wholesaler as an intern. After that, Hattori worked at a clock shop where he learns the tactics to sell and also learned clock repairing. Kintaro successfully runs Seiko till his death in 1934. The Japanese pioneer who launched the Japanese wristwatch brand in competition with the famous Swiss died when he was 73.
Best of the Seiko
In 1960, the next and all-time popular model Grand Seiko was launched. It was the next version of one more famous watch Crown.
Seiko is known for the quartz watch model called Astron. This model was introduced in 1969 which also became the first quartz watch on earth.
Thereafter, the company launched a quartz chronograph for the first time ever. Seiko didn’t stop here and further launched automatic quartz for the first time.
After a huge success, the firm started a joint manufacturing unit with Orient and so established in 1985.
However, these all watch models were again launched in 1991 under the name Seiko kinetic.
Official timekeeper
Seiko made in the list of best watchmakers with its one more achievement. It has been the official timekeeper in several international sports events. The FIFA World Cup, Olympics, and now signed an agreement with IAAF for being the official timekeeper in the next IAAF World Championships.
Bottom line
A Japanese company Seiko is recognized for launching leading watch brands in the market. Especially, it is best known for the exclusively made wristwatches. Apart from manufacturing watches, the firm is also known as a one-stop solution for clock and watches. It means, Seiko produces all the parts of watches like rock crystal oscillators, sensors, LCDs. As well, one can get the lubricants needed for watches.
Seiko is continuing its legacy, dedication, and perfection with its plus 130 years of innovation. It has become a name that is known to everyone and competing with the best in business. In 2001, , the firm becomes a holding company since 2001. The company has definitely come a long way from launching the basic product to the best one. We can definitely say that Seiko is a timeless business venture of K. Hattori. Something that you learn in life at earlier stage or later, always helps you to build big dream for yourself.

Jayshri is an Electronics Engineer, but her passion towards writing made her to be in this field. Apart from content writing, she loves reading, writing and surfing on various topics. In her free time, she likes to watch TV series and news. Sherlock Holmes is her all time favorite show. Jayshri loves cooking various Indian-western dishes.